When working with Large Language Models (LLMs), it is essential to understand specific key parameters that influence the model’s behaviour. Two of the most critical parameters are:
- Temperature
- Top-P (nucleus) sampling value
Temperature is a parameter that controls the randomness in the model’s output by affecting how the model selects the next token to generate.
The value of temperature varies between 0 and 2.
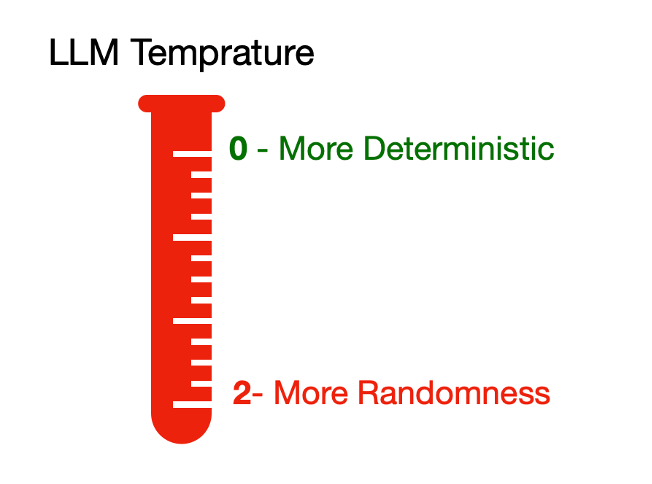
The temperature parameter of an LLM,
- Controls the next word prediction
- Its value ranges from 0 to 2
- The lower temperature value produces a more deterministic response
- The higher temperature value produces a more random or creative response
How does temperature work?
When an LLM generates text, it assigns probabilities to possible next words using a softmax function:
P(word) = exp(logit/T) / Σ exp(logits/T)
Here,
- T – it’s a temperature value.
- Logits – It is the raw, unnormalized output scores that a model produces before they are converted into probabilities.
It is a good idea to keep the value for the temperature parameter as mentioned below:
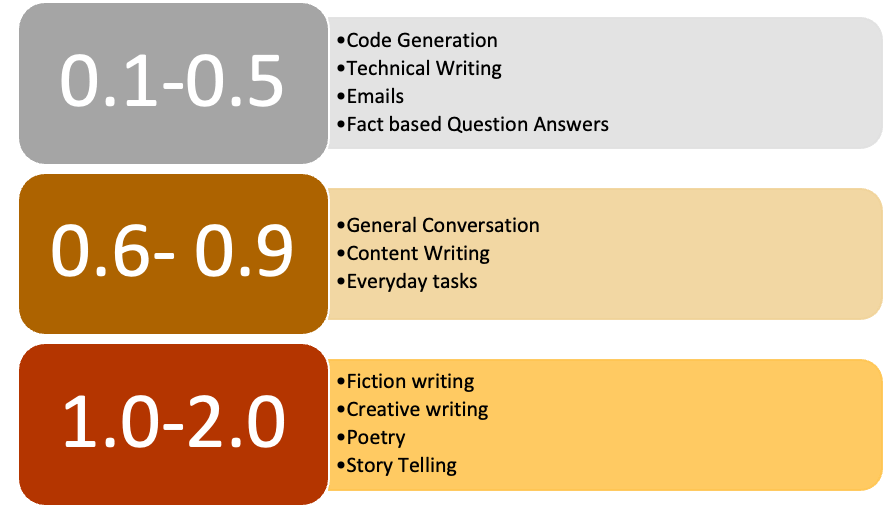
While working with a model, you can pass the temperature value as shown below :
openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Write a Python function"}],
temperature=0.2
)
In subsequent posts, we will delve into the details of tuning different temperature values to achieve the expected generated response.
I hope you now have a basic understanding of the temperature parameter of models. Thanks for reading.
Discover more from Dhananjay Kumar
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
2 thoughts on “GenAI for Beginners: What is the Temperature parameter in a model”